In this article, we will look at XCP-ng vs Proxmox. Whether you use XCP-ng or Proxmox, they are both hypervisors that allow you to run virtual machines (VMs). These virtual machines are separated from the physical hardware (RAM, CPU, and other physical resources) through a virtualization layer.
By sharing their resources virtually, XCP-ng and Proxmox allow the underlying hardware of a host machine to run one or more virtual machines as guests independently.
There are many benefits to a hypervisor, including separating the operating system (OS) from the application, virtualizing a crucial management layer, and controlling the environment of a data center and enterprise.
XCP-ng vs Proxmox: Which Hypervisor Should You Use?
This article will cover a side-by-side comparison of XCP-ng vs Proxmox and compare some of the differences between performance, pricing, and functionality. We’ll look at exactly what XCP-ng and Proxmox are before comparing them and helping you pick between XCP-ng or Proxmox.
What is the XCP-ng Hypervisor?
XCP-ng is an enterprise open-source server virtualization platform that was initially based on XenServer. XCP-ng is based on CentOS, unlike Proxmox which is based on Debian GNU/Linux. XCP-ng is also a powerful XAPI (Xen API Project), which works out of the box to deliver turnkey in-server virtualization.
XCP-ng is compatible with 64-bit x86 servers, supports up to 5TB of RAM, 16 physical NICs, and up to 288 logical processors per host. XCP-ng is built on top of components of the Linux kernel (GPLv2). Since it’s open source, its dev process, documentation, repositories, and components are easily accessible and publicly available.
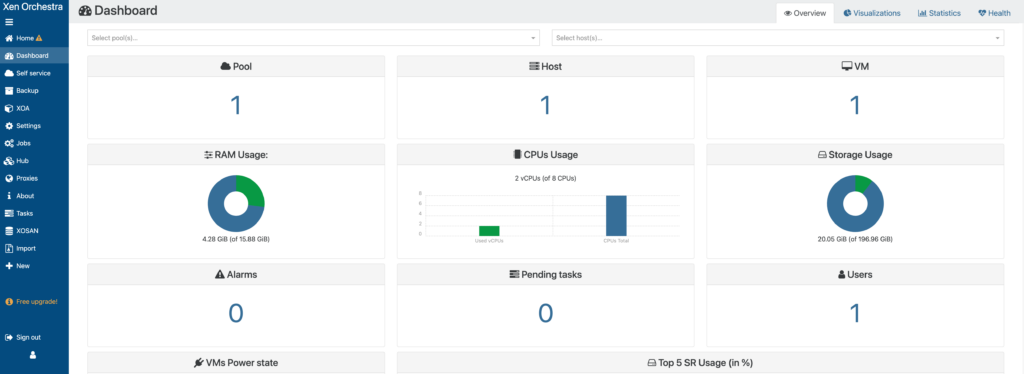
Features of XCP-ng
Below is a list of some of the best features of XCP-ng:
Multi-Server Management
The multi-server management feature of XCP-ng enables you to manage, monitor, and administer all of your data and infrastructure using a single agentless web interface.
Live VM Migration
Live VM migration is another perk of XCP-ng that allows you to migrate your virtual machines (VMs) live with little downtime.
Live Patching
The live patching ability of XCP-ng allows you to patch the XCP-hypervisor without suspending or shutting down VMs. You also aren’t forced to migrate your VMs from the host.
Storage Migration
The storage migration feature of XCP-ng enables you to move your virtual disk within and across the resource pools. It also helps you adapt, maintain, and administer your storage and infrastructure without downtime.
Accelerated Performance
XCP-ng works with the Xen Orchestra Web UI and XCP-ng Center (Windows-based), allowing you to manage, monitor, and administer all your data and infrastructure from a single interface.
What is Proxmox Virtual Environment?
Proxmox Virtual Environment (VE) is a hypervisor (type-1) that runs directly on the hosts hardware and is used to create VMs and LXC containers. It is Debian-based, free, publicly accessible, and enterprise-class virtualization.
Like XCP-ng, Proxmox is an open-source server virtualization management solution that enables users to utilize KVM virtualization. Proxmox VE is easy to install and offers an easy-to-use web interface for containers and VM management (virtual machines), and associated resources on Proxmox nodes and clusters.
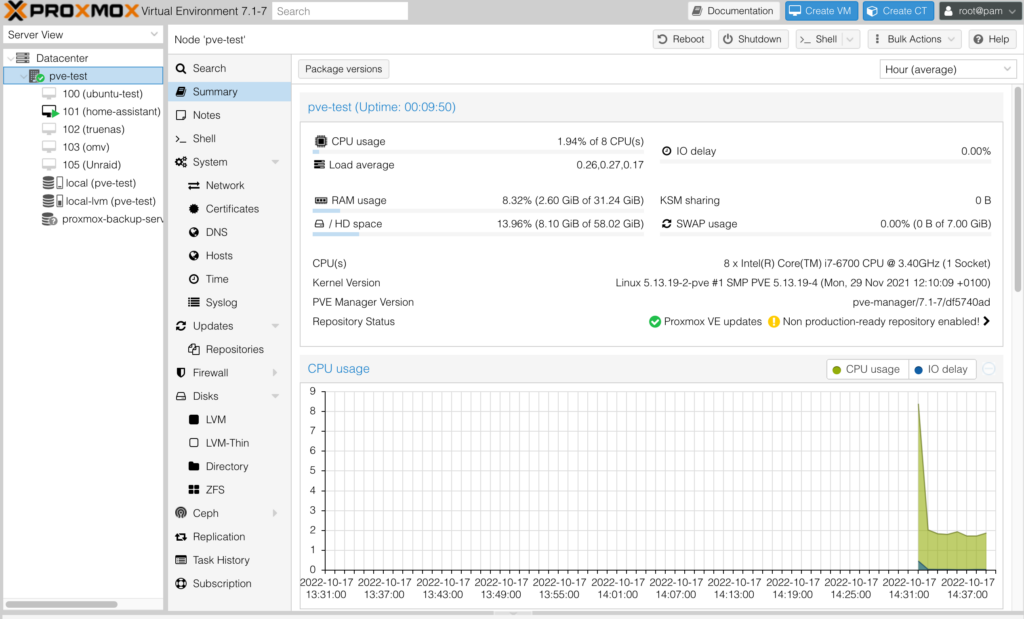
Features of Proxmox VE
Below is a list of some of the best features of Proxmox:
Live VM Migration
Through Proxmox’s live migration feature, users are able to move running virtual machines from one node on a cluster to another without experiencing any perceivable downtime.
Multiple Authentication Sources
Proxmox VE has an integrated authentication server with numerous authentication sources including the OpenID Connect authentication protocol, LDAP, Microsoft Active Directory, and Linux PAM.
Multiple Storage Options
The storage options of the Proxmox virtual environment are highly flexible. The web interface of Proxmox allows users to add multiple storage types, such as CephFS, GlusterFS, SMB/CIFS, iSCSI, and NFS shares (which can also be used for backing up VMs or Containers).
IT Infrastructure Protection & Scheduled Backups
With Proxmox VE, you can protect your IT infrastructure by using a built-in firewall. Proxmox allows for complex firewall configurations through the CLI or GUI. Proxmox also gives users the ability to set up scheduled backups for VMs, nodes, and guests which run automatically based on the schedule specified.
Granular Access & Collaboration with Ceph
Proxmox VE provides full integration with Ceph, giving users access to and control over Ceph storage directly from their cluster nodes. Users are able to define granular access to all objects using Proxmox VE’s role-based permission management system.
Pricing Plans Between Proxmox and XCP-ng
The pricing plans of XCP-ng don’t have feature restrictions or license fees. You only pay for support.
| Plan | Cost and Available Features |
|---|---|
| Standard | $600 per host & per year – SSH pro support – Six support tickets per year – One business day response time |
| Enterprise | $1,200 per host & per year – SSH pro support – Upgrade assistance – Linux drivers integration – XCP-ng devs direct access – Initial setup assistance – 1-hour response time – Unlimited support tickets |
The free version of Proxmox supports several features, but you must have a paid subscription to access technical support and enterprise repositories.
| Plan | Cost and Available Features |
|---|---|
| Community | Starts from ~$95 (€95) per year & CPU socket |
| Basic | Starts from ~$295 (€295) per year & CPU socket. Three support tickets per year. |
| Standard | Starts from ~$445 (€445) per year & CPU socket. Ten support tickets yearly. |
| Premium | Starts from ~$890 (€890) per year & CPU socket. Unlimited support tickets. |
When comparing the pricing between XCP-ng vs Proxmox, there isn’t a significant difference, so other factors should sway your decision.
Feature Comparison: XCP-ng vs Proxmox
We will look at an overall feature comparison of XCP-ng vs Proxmox below.
Advantages of XCP-ng
- Enterprise Virtualization Platform (Proxmox is not an enterprise virtualization platform)
- Stability and uptime
- Nested virtualization
- Xen Orchestra (must be installed)
- Improved network management through GUI
- Cross-cluster resource migration for both VDIs and VMs
- Removable nodes
- Clustering with up to 64 nodes
- Scheduled and automatic snapshots
Advantages of Proxmox
- Web GUI is installed by default (XCP-ng must install Xen Orchestra or XCP-ng Center for web GUI)
- 2-way data replication for local storage
- LXC container support
- Unlimited number of snapshots for virtual machines (VMs)
- Simple management process
- Standard Linux distribution
- ZFS support
Main Differences Between XCP-ng and Proxmox
The main difference between XCP-ng and Proxmox is that XCP-ng uses Xen Hypervisor and is built on CentOS, while Proxmox uses KVM and is built on Debian GNU/Linux. These are significant differences when it comes to user interaction and the decision on which to use can solely be based on operating system comfort in certain cases.
The chart below highlights some other key differences between XCP-ng vs Proxmox.
| XCP-ng | Proxmox | |
|---|---|---|
| Based On | Derived from XenServer, a commercial type-1 hypervisor product by Citrix. | Based on Debian, a popular Linux distribution. |
| Virtualization Type | Primarily a Xen-based type-1 hypervisor. Supports paravirtualization and full virtualization. | Uses KVM and container-based virtualization with LXC. |
| Interface | Primarily managed via Xen Orchestra or CLI, but also has a basic GUI. | Provides a web-based GUI and CLI for management. |
| Backup | Provides a range of backup options via Xen Orchestra, including continuous replication. | Supports snapshot, backup, and live migration. |
| Storage | Supports local storage, NFS, iSCSI, and Fibre Channel. | Supports local storage, NFS, iSCSI, Ceph, and GlusterFS. |
| Networking | Provides network bonding, VLANs, and the option for software-defined networking with Open vSwitch. | Offers network bonding, VLANs, and software-defined networking with Open vSwitch. |
| High Availability | High availability can be achieved using clustering and pool features. | High availability is supported with Proxmox VE Cluster. |
| Community & Support | Open-source with active community support. Commercial support is available. | Open-source with a strong community. Commercial support is available. |
Performance Differences
When comparing the performance between XCP-ng vs Proxmox, XCP-ng and Proxmox offer exceptional overall performance as hypervisors. They are both compatible with various types of hardware and offer similar performance based on the hardware that they’re using.
Please keep in mind that XCP-ng and Proxmox are hypervisors, meaning that they are meant to be installed on bare metal. This allows you to run virtual machines (and in Proxmox’s case, LXC containers) on them. If you install XCP-ng and Proxmox on the same exact hardware, you’ll be happy with either from a performance perspective.
In general, when comparing XCP-ng vs Proxmox, both hypervisors offer great performance.
Backup and Replication
There aren’t major differences when comparing the backup and replication features between XCP-ng vs Proxmox.
XCP-ng provides a comprehensive set of backup features aimed at enhancing data protection and disaster recovery in virtualized environments. Among the key features are automated snapshots, full VM backups, forever incremental backups, and disaster recovery capabilities.
XCP-ng also supports continuous replication of VM changes to a backup repository and metadata backups to preserve vital VM information and configurations. The platform also offers file-level restore capabilities, enabling the recovery of individual files or directories.
Proxmox offers a fully integrated backup solution as well, supporting different backup modes for VMs and containers, scheduled backups, and a live-restore option to reduce downtime during restoration. It also allows setting bandwidth limits for backups, specifying file exclusions, and defining global configurations.
Additionally, Proxmox provides backup compression, encryption, and retention options. Unique features like protected backups, adding notes to backups, and hook scripts for custom actions are also supported.
Proxmox also has its own backup tool, called Proxmox Backup Server, which allows users to set up backup schedules that are either full or incremental.
Conclusion: Should you use XCP-ng or Proxmox?
This article looked at XCP-ng vs Proxmox to determine which hypervisor is best. From a pure hypervisor perspective, I’ve always preferred Proxmox due to its ease of use. However, I’ve been extremely happy with XCP-ng lately and it’s important to remember that XCP-ng is an enterprise virtualization platform, while Proxmox isn’t, so the chances are high that you’ll be happy with XCP-ng or Proxmox.
I still run Proxmox in my production environment, but I’m considering switching to XCP-ng, which is a true testament to the platform and proves that Proxmox isn’t necessarily better than it. Both systems support various features and serve different purposes in server virtualization, but overall, you’ll most likely be happy with either.
Thanks for checking out the article on XCP-ng vs Proxmox. If you have any questions on, please leave them in the comments!




