In this article, we’re going to look at pfSense vs. OPNsense. pfSense and OPNsense are both firewalls that have many similarities, but also a bunch of differences. Overall, they both will function as great firewalls and allow you to set up various types of things like VLANs, VPNs, and more.
These are two of the most popular firewalls that you can use, especially due to how powerful they are when properly configured, but we’ll compare them below to help you decide which firewall is best for you.
A few disclaimers before we get started comparing pfSense vs. OPNsense:
- pfSense and OPNsense are both excellent. Overall, you’ll most likely be happy with either, pfSense or OPNsense, but there are differences you should consider.
- If you have a hypervisor of some sort and a supported network card, you can virtualize both firewalls (pfSense and OPNsense) to determine which you like best.
- I have a bunch of tutorials on pfSense and OPNsense, so please check them out!
What is pfSense and What Does it Offer?
pfSense is a free, open-source firewall and router based on FreeBSD, created and maintained by Netgate. pfSense is as customizable as you want it to be, meaning that you can simply use it as a basic firewall and DHCP server, or customize it thoroughly and create VLANs, install packages, and even run WireGuard or OpenVPN on it to ensure you can access your network from anywhere.
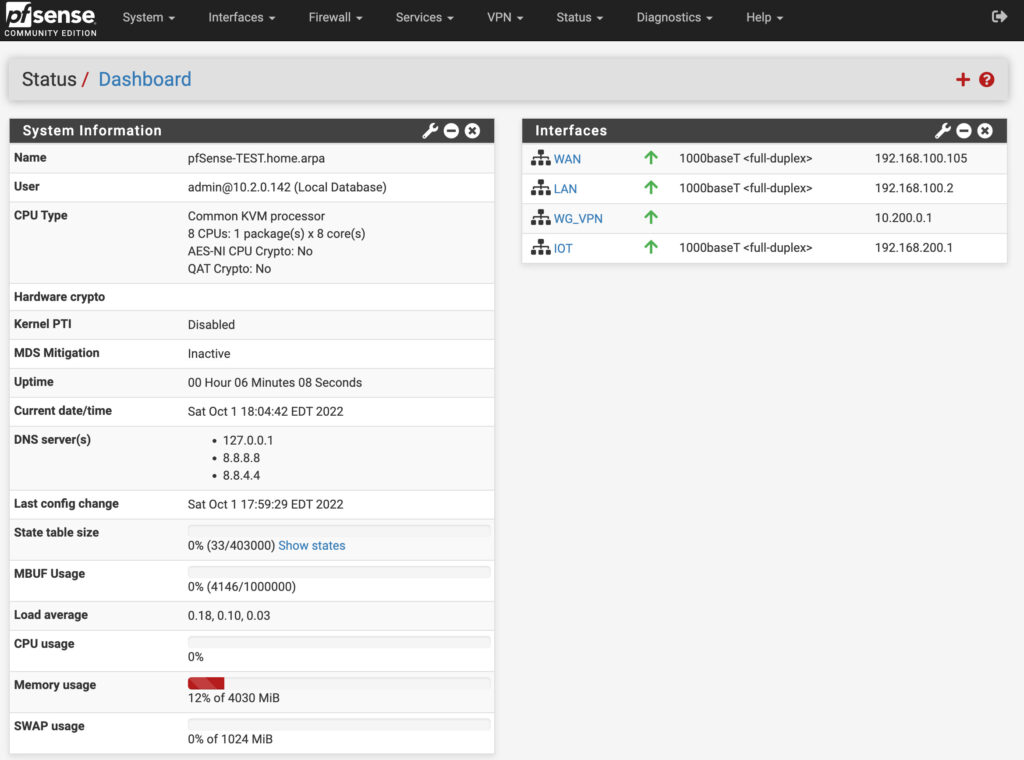
While pfSense can be installed on older hardware or even virtualized, Netgate does sell devices that you can purchase which are extremely powerful and come with pfSense preinstalled. They also come with pfSense Plus included at no charge, whereas pfSense Community Edition is the version used for personal hardware.
One of the best things about pfSense is that there’s a really great community behind it, so if you have a question, want to implement something new, or need to learn how to troubleshoot an issue, there’s a great group of people who are willing to help.
Features of pfSense
Below is a short list of some of the features that pfSense provides.
Firewall:
- Uses Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) to track and filter network connections.
- Provides IP/DNS-based filtering and Anti-Spoofing for added security.
- Allows for a captive portal guest network.
- Supports time-based rules and connection limits.
- Includes NAT mapping for inbound/outbound connections.
Router:
- Supports policy-based routing, concurrent IPv4 and IPv6, and configurable static routing.
- Handles IPv6 network prefix translation and router advertisements.
- Supports multiple IP addresses per interface.
- Includes a PPPoE server.
Attack Prevention:
- Features IDS/IPS and a Snort-based packet analyzer for attack detection.
- Uses Layer 7 application detection and maintains an emerging threats database.
- Provides application blocking and deep packet inspection (DPI).
- Allows per-interface configuration and false positive alert suppression.
VPN:
- Supports IPsec, OpenVPN, and Wireguard VPN protocols.
- Enables site-to-site and remote access VPN with SSL encryption.
- Compatible with multiple OS VPN clients and L2TP/IPsec for mobile devices.
- Supports split tunneling, multiple tunnels, VPN tunnel failover, and NAT support.
- Allows local user authentication or RADIUS/LDAP.
Proxy and Content Filtering:
- Provides HTTP and HTTPS proxy services.
- Offers domain/URL filtering, anti-virus filtering, and SafeSearch for search engines.
- Supports website access reporting, domain name blacklisting (DNSBL), and usage reporting.
Network Services:
- Includes Dynamic DNS, DHCP Server, and DNS forwarding.
Configuration Management:
- Features web-based configuration with setup wizard and remote web-based administration.
- Offers easy backup/restore, export/import of configurations.
- Supports multi-language and simple updates.
- Provides serial console for shell access and recovery options.
- Includes a Wake-on-LAN feature.
User Authentication Management:
- Maintains a local user and group database with user and group-based privileges.
- Supports optional automatic account expiration and external RADIUS authentication.
- Provides automatic lockout after repeated failed attempts.
System Security Management:
- Provides web interface security protection, CSRF protection, and DNS Rebinding protection.
- Supports HTTP Strict Transport Security and optional key-based SSH access.
Resilience/Reliability Management:
- Supports optional multi-node High Availability Clustering and multi-WAN for load balancing/failover.
- Offers reverse proxy and automatic connection failover.
- Provides bandwidth throttling, traffic shaping, and user data transfer quotas.
System Reporting and Monitoring:
- Provides a dashboard with configurable widgets and local/remote logging.
- Offers local monitoring graphs, real-time interface traffic graphs, and SNMP monitoring.
- Includes hardware monitoring and networking diagnostic tools.
- Sends notifications via web interface, SMTP, or Growl.
What is OPNsense and What Does it Offer?
Similar to pfSense, OPNsense is a free and open source FreeBSD-based firewall, created by Deciso. OPNsense has many of the same features as pfSense, but an entirely different GUI which we’ll take a look at below. Deciso sells hardware that you can purchase which comes pre-installed with OPNsense, but can also be installed on personal hardware or in a virtual machine.
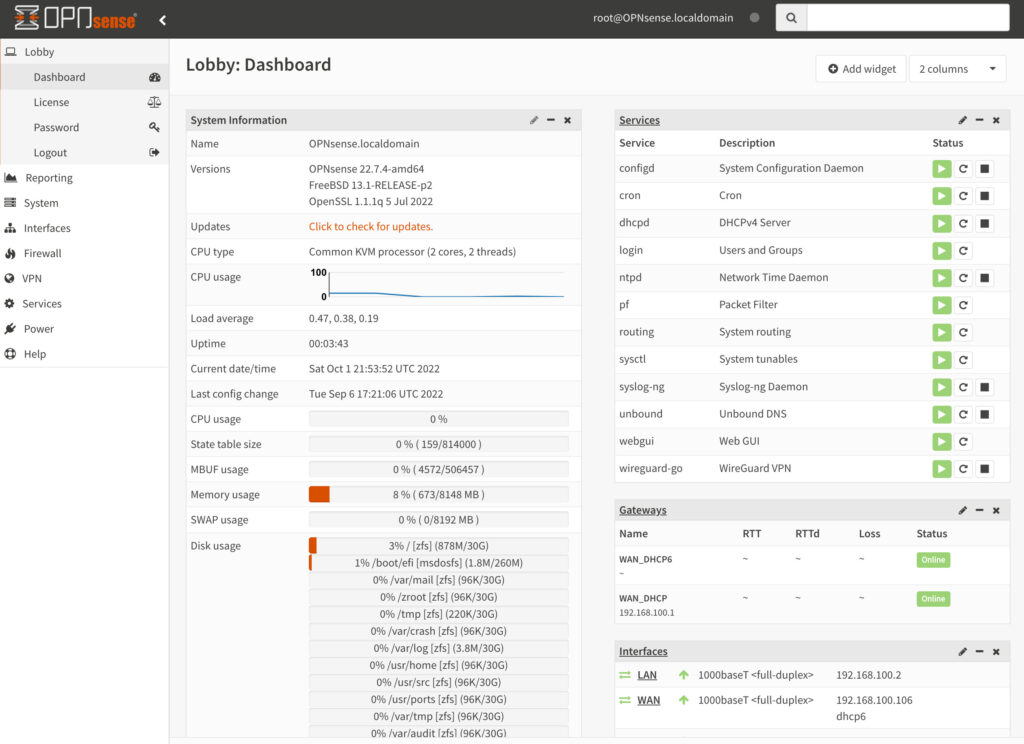
OPNsense is extremely customizable and has a bunch of different things you can configure, from VLANs to VPNs, and generally, is extremely user-friendly. We will look at some of that user-friendliness below.
Features of OPNsense
Below is a short list of some of the features that OPNsense provides.
Traffic Shaper:
- Allows prioritization of network traffic for improved performance.
Captive Portal and Voucher Support:
- Provides a captive portal for network access control.
- Supports vouchers for time-limited network access.
Template Manager and Multi Zone Support:
- Offers a template manager for consistent configurations.
- Supports multiple zones for segmented network control.
Forward Caching Proxy:
- Includes a forward caching proxy for faster web service delivery.
- Supports transparent mode and blacklist management.
Virtual Private Network (VPN):
- Supports site-to-site and road warrior VPN configurations.
- Provides support for IPsec and OpenVPN protocols.
High Availability & Hardware Failover:
- Features configuration synchronization and synchronized state tables.
- Supports moving virtual IPs for improved network flexibility.
Intrusion Detection and Inline Prevention:
- Offers built-in support for Emerging Threats rules.
- Simplifies setup with rule categories and scheduled automatic updates.
Reporting and Monitoring Tools:
- Features system health monitoring and packet capture tools.
- Supports Netflow for network traffic analysis.
- Allows for extended functionality with plugin support.
DNS Server & DNS Forwarder:
- Includes DNS server and forwarder for network name resolution.
DHCP Server and Relay:
- Offers a DHCP server and relay for IP address management.
Dynamic DNS:
- Supports dynamic DNS for handling changing IP addresses.
Backup & Restore:
- Provides backup and restore capabilities.
- Supports encrypted cloud backup to Google Drive and Nextcloud.
- Includes configuration history with colored diff support.
- Allows local drive backup & restore.
Stateful Inspection Firewall:
- Utilizes a stateful inspection firewall for improved network security.
- Provides granular control over the state table.
- Supports 802.1Q VLAN for network segmentation.
pfSense vs. OPNsense: Firewall Comparison
We will break down different categories below to compare both options and help you decide if pfSense or OPNsense is better for you.
User Interface
No matter what system you’re using, the user interface is extremely important as it’s what you use to interact with the system. While pfSense has a clean user interface, I tend to find OPNsense easier to use and more logical, meaning that things are where you’d expect them to be. In OPNsense, you navigate through the settings by using the menu bar on the left side of the screen.
pfSense has a menu bar at the top that will allow you to navigate through the system, but the overall function is slightly more confusing (in my opinion).
Where OPNsense feels logical, pfSense feels clunky. That’s not to say that it’s bad (as a lot of those extra menu items are used for customization), but there have been times when it’s taken me longer to find what I’m looking for than it probably should. This is mostly due to the fact that there are a lot of menu options in pfSense. That could be a good or bad thing depending on how you like to operate.
Usability
Both are extremely similar when it comes to usability. That’s a good thing, as switching from one to the other will mean that you’re fairly familiar with the system and will be able to figure everything out.
The main differences come when you first start using each firewall. pfSense and OPNsense are extremely different than most consumer-grade routers and firewalls. Even things that are fairly simple like port forwarding have a lot more settings on pfSense/OPNsense. There is a learning curve to both of these systems, but you’ll find quickly that all of the options make sense.
It’s also important to note that these additional settings are what make pfSense and OPNsense so great, but it will be slightly confusing the first time you use them and you’ll probably have to reference documentation to ensure you’re doing everything correctly.
The GUI does make OPNsense slightly more usable, but you’ll find that the usability benefits are really just from a navigational standpoint. Overall, they both are extremely powerful and due to that, tend to have more confusing settings than some may expect. While this may sound like a negative, it’s a huge positive.
Feature Differences Between pfSense and OPNsense
pfSense and OPNsense both offer various features that are fairly standard from a firewall perspective, but we’ll look at some of the key features below.
Feature Differences
| Features | pfSense | OPNsense |
|---|---|---|
| Load Balancing and HA | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Dual WAN | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Network Address Translation (NAT) | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Firewall Management | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| VLAN Support | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| DHCP / DNS Configuration | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| DDNS Setup | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Fork History | Fork of mOnOwall from 2004 | Fork of pfSense from 2015 |
Load Balancing and HA
pfSense and OPNsense offer load balancing and high availability (HA). In general, HA can be configured using the LAN and/or WAN interfaces. It’s generally configured with a Sync interface that allows the firewalls to synchronize configurations and states between the primary and secondary firewalls.
From an enterprise perspective, this is a requirement, as redundant hardware is necessary for a resilient network.
Dual WAN
pfSense and OPNsense both allow you to have Dual-WAN configurations that can provide maximal internet uptime.
While it’s generally a best practice to configure Dual-WAN with Load Balancing/HA (shown above), Dual-WAN will give users the ability to provide maximal uptime from a WAN perspective only without having redundant Firewall/Switch hardware.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
pfSense and OPNsense both provide Network Address Translation functionality which allows you to expose an individual server/service to the outside internet. You can complete this by utilizing port forwarding on pfSense or OPNsense.
Firewall Management
pfSense and OPNsense come with highly customizable firewall configuration tools that allow you to create specific pfSense or OPNsense firewall rules. These rules can be configured on each interface allowing users to separate traffic between physical or virtual (VLAN) interfaces.
VLANs
There aren’t many differences when comparing VLANs in pfSense and OPNsense. Both devices allow you to set up virtual LANs to separate traffic on your local network. Paired with the Firewall, you can determine which VLANs can/cannot communicate with each other.
DHCP / DNS
pfSense and OPNsense can be configured as a DHCP server and/or a DNS server. The DHCP server allows the firewall to automatically hand out IP addresses to internal servers.
pfSense and OPNsense both utilize Unbound DNS which functions as a validating, recursive, and caching DNS resolver. The goal of Unbound is to be fast and lean, and generally provide the best DNS performance possible.
While you can use Unbound (and most people should), you can also use upstream DNS providers (like Google or Cloudflare). They both also give you the option of using both, meaning Unbound can be used as a primary DNS resolver with an upstream DNS provider being used as a secondary option if Unbound fails.
DDNS
Setting up a DDNS hostname in pfSense or OPNsense is extremely simple, but very important for some users.
DDNS hostnames allow you to ensure you’re always accessing the external IP address of a network when an ISP provides a dynamic IP address rather than a static IP address.
Forks
The features above for pfSense and OPNsense are fairly similar because they’re both, directly and indirectly, forks of mOnOwall. pfSense is a fork of mOnOwall from 2004 (and officially released in 2006), while OPNsense is a fork of pfSense from 2015.
Packages & Plugins
In pfSense or OPNsense, you can install various different applications that will help customize your experience.
Packages in pfSense
Plugins/Packages in OPNsense
A lot of the packages and plugins that you can download are similar. Whether you want to run WireGuard in pfSense or OPNsense, set up a UPS server, manage certificates, or do tons of other things, you can probably do it in both.
There are differences between the packages (like pfBlockerNG existing on pfSense only), but they’re so user-specific that I highly suggest that you search exactly what you’d like to implement and confirm that pfSense/OPNsense has it before deciding which firewall to use.
I do want to be clear that this is one of the biggest differences. pfSense and OPNsense have extremely similar offerings by default, so you need to ensure that the packages/plugins that you’d like to use (if you’d like to use them), exist on the software.
VPN Servers
If you’re interested in setting up a VPN on pfSense or OPNsense, both will both allow you to do it relatively easily. I did find the process of installing WireGuard slightly easier on OPNsense, but I have tutorials on pfSense and OPNsense which will help you get up and running quickly.
pfSense and OPNsense will allow you to set up IPsec, OpenVPN, and WireGuard VPNs.

They’re also extremely customizable and allow you to set up servers and clients (in OpenVPN, for example), which means that you can set up site-to-site VPNs easily, or even connect to other VPNs as well.
One cool thing that I’ve set up (and plan on creating a tutorial for) is NordVPN on pfSense/OPNsense. After NordVPN is configured as a client, you can specify an IP range or subnet and route all traffic through that VPN. No more authenticating on client devices!
Site-to-Site VPNs
While you can configure an individual VPN, you can configure site-to-site VPNs as well. There are various ways to do this, with IPsec, OpenVPN, and WireGuard all being options.
This allows you to easily connect two separate firewalls (at two different locations) to each other and route traffic back and forth.
Differences Between pfSense and OPNSense
The main differences when comparing pfSense and OPNsense are in their user interface and update schedules, as pfSense targets three releases per year, while OPNsense schedules two major releases each year, with security updates every two weeks.
The operating system on which pfSense and OPNsense are built on used to be a difference as well (with OPNsense using HardenedBSD), but that is no longer a difference as of 2024, as pfSense and OPNsense are both built on FreeBSD.
The update schedule is a significant difference as firewall updates can bring down the entire network that they’re used on during the update process. There are also risks with updates in general, as they can lead to potential issues that weren’t discovered during testing (though clearly, there are benefits too).
Fortunately, OPNsense does a good job with security updates and this can be viewed as a good thing in certain cases. However, in an enterprise environment, the updates that pfSense releases will be easier to manage.
Popularity & Interest
When doing comparisons, I always like to show their overall interest for the prior year from a Google search perspective (using Google Trends) to help you decide if you should pick pfSense or OPNsense for its community. This is because the popularity of a product can lead to better support and interaction from other users.
The chart below shows the overall interest over time from a search perspective, comparing pfSense and OPNsense for the prior year, worldwide.
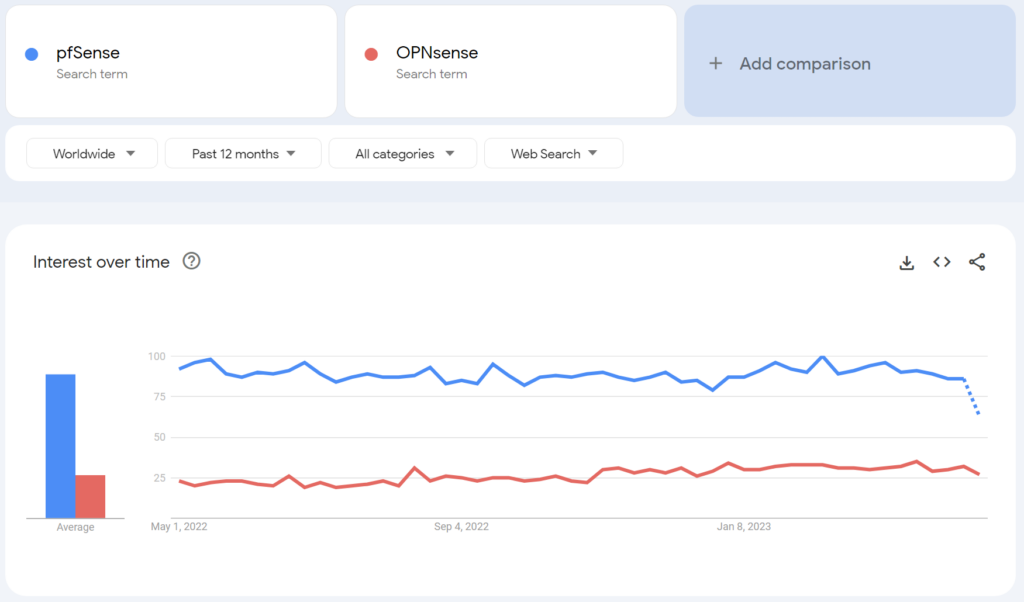
From a global perspective, pfSense is drastically more popular and searched for than OPNsense and it’s consistent.
While this doesn’t mean that you should pick pfSense over OPNsense (for this reason and this reason alone), it does mean that there will be more users, guides, tutorials, and troubleshooting information online for pfSense than there are for OPNsense.
Conclusion & Final Thoughts: pfSense or OPNsense?
When comparing pfSense vs. OPNsense, overall, I think that most people will be extremely happy with both of these firewalls which I’ve mentioned a few times in this debate.
While I prefer the OPNsense GUI, I don’t necessarily think that pfSense is hard to use. It’s just a nod to the developers that configured the OPNsense GUI, as they packed a bunch of powerful settings into a pretty easily understood user interface.
It’s hard to pick which is better because there really isn’t a better choice in my opinion. Both options are extremely powerful and depending on your goals, you might prefer one over the other, but that doesn’t make the other option bad.
For moderate to advanced firewall configurations, you’ll most likely be able to use either and be happy. The differences really come with some of the packages, so I’d suggest that you take the time to think about what you’d like to do (or learn about some of the different options) and go from there.
Once again, if you have an older PC or hypervisor, you can install both and play around with them to try and determine which you like best! This will help you compare them yourself to learn which you prefer!
Thanks for checking out the article on pfSense vs. OPNsense! If you have any questions, feel free to leave them in the comments!




