In this article, we’re going to look at what is the best RAID type For a Synology NAS.
One of the main reasons to set up a NAS is to be able to utilize redundancy. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks and allows individual disks to work together to create a large storage pool. After configuring a RAID array, you will have multiple hard drives working together with the potential for redundancy.
We will look at some common RAID types below with the goal of explaining the best options from a consumer and general perspective, without diving too deep into the technical specifications. After selecting one of the options, make sure you look at the differences between Btrfs vs. Ext4 for your volume configuration!
What is the Best RAID Type for a Synology NAS?
I want to be clear that the explanations are my opinion and it’s best to understand your options, and then select the best RAID type based on the requirements.
RAID is not a backup! Make sure that you take proper backups or you run the risk of data loss!
RAID 0
RAID 0 is something that (in my opinion) should never be used for NAS devices. It works by splitting data across multiple drives, which means that you’ll get the total drive space allotted, but you will not have redundancy. This means that if any hard drive fails, you will lose all of your data.
From an actual NAS perspective, RAID 0 is normally allowed, but generally ill-advised. If you’re setting up a NAS, it’s best to have some form of redundancy, which is why I recommend you use one of the options below. There are performance benefits to RAID 0, but overall, the lack of redundancy is why I don’t recommend it for most.
RAID 1
RAID 1 mirrors data, which means that when data is written to the first hard drive, it’s also written to the second hard drive. This ensures that redundancy exists and that if one hard drive fails, the other will still contain the data. You should use two equally sized hard disks with RAID 1, or the smaller disks size will be used (meaning if you use a 4TB and 6TB drive, you’ll only have 4TB of usable space).
From a NAS perspective, RAID 1 is beneficial if you have a Synology NAS device with two bays. If you have more, it generally isn’t used as you’ll be able to utilize more hard drive space with another RAID type.
RAID 5
RAID 5 is the option that most users will use (or SHR, which we’ll look at below) and is generally a great option for NAS devices with less than five drive bays. If you have a NAS device with six drive bays, you can certainly use this, but you might also benefit from RAID 6.
RAID 5 works by saving one hard drive for redundancy, meaning that one hard drive can fail at any time without data loss. If a hard drive fails, you can replace it and the array will rebuild the new drive. After the drive rebuilds, you will be able to have any hard drive fail again without data loss. If two hard drives fail at the same time, you will lose all data.
RAID 5 is a great option for most Synology NAS devices, but you must ensure that you use the same sized hard drive or the smallest disk size will be used (three 6TB hard drives and one 4TB hard drive will result in 12TB of usable space and 4TB saved for redundancy).
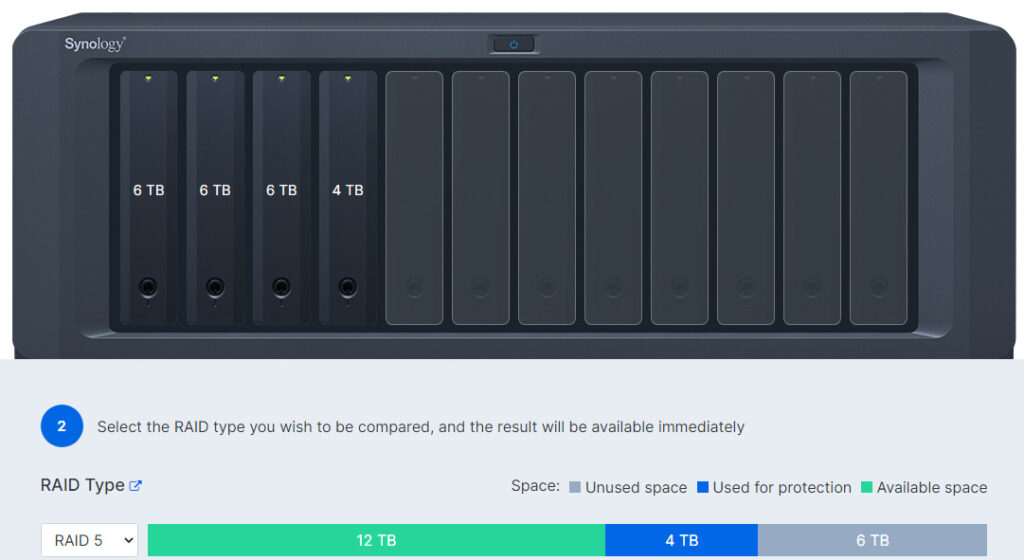
SHR
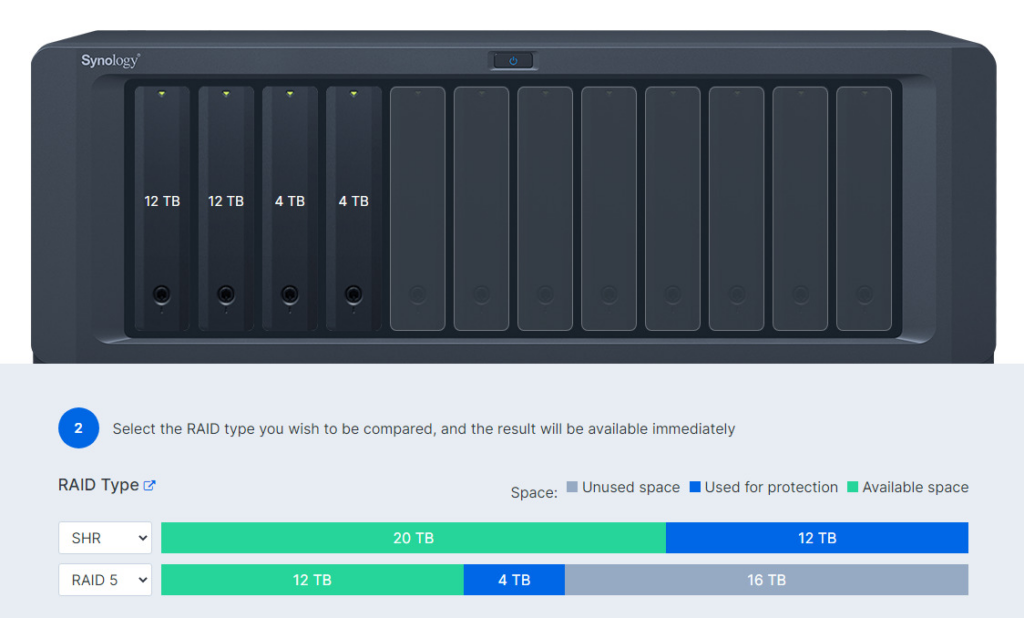
Synology Hybrid RAID is an automated management system, which is a fancy way of saying that you will have the flexibility to use different-sized hard drives in an array, while actually utilizing some of the storage space. SHR is based on a Linux RAID system.
To demonstrate SHR using the example below (with Synology’s RAID calculator), you’ll see that two 12TB hard drives and two 4TB hard drives will give you 20TB of usable space with SHR but only 12TB of usable space with RAID 5. The reason is that RAID 5 can only utilize the smallest-sized hard drive in the array, so all other hard drives will be limited to the smallest-sized drive. For that reason, in RAID 5, it’s in your best interest to use the same-sized hard drives.
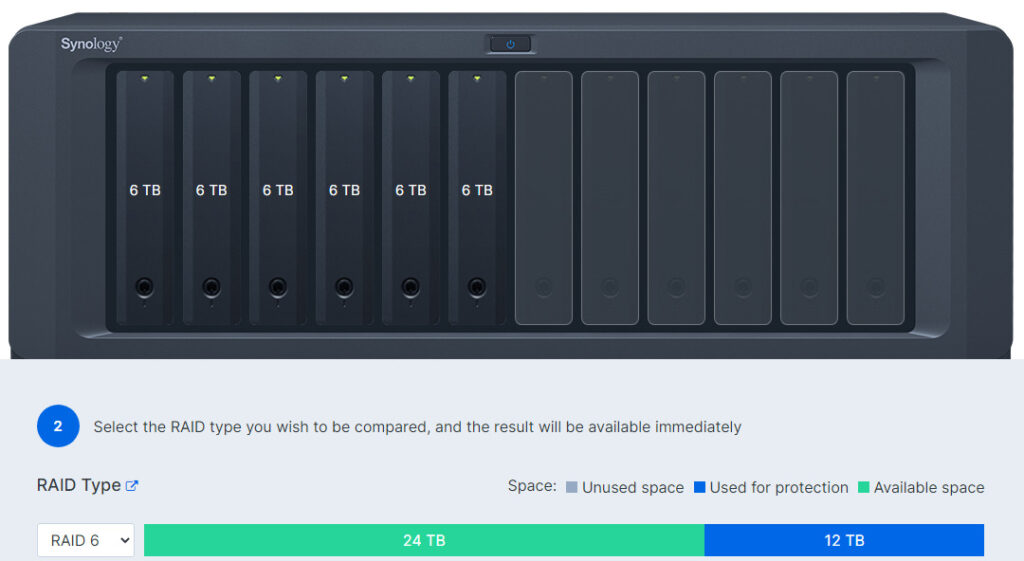
RAID 6
RAID 6 is extremely similar to RAID 5, but you will have two total hard drives that can fail before data loss rather than one. Generally, RAID 6 is a waste for NAS devices that have less than six drive bays as you’ll be allocating too many hard drives for redundancy.
However, six-bay devices are generally the tipping point where you might want to start considering RAID 6. There is a slight performance hit for write operations with RAID 6 due to the extra parity calculations, but not enough for it to impact your decision on its usage.
If you have a NAS device that has at least eight drive bays, you should certainly be using at least RAID 6/SHR-2. At that point, RAID 10 (which we will look at below) is an option as well, but RAID 6/SHR-2 is the starting point.
SHR-2
SHR-2 has the same functionality as SHR but with two drives of redundancy as opposed to one. The same principles of SHR apply, and you should certainly use Synology’s Calculator to determine how much storage space you’ll have available if you go down this path.
While SHR is comparable to RAID 5, SHR-2 is comparable to RAID 6, with both, SHR and SHR-2 allowing for mix-sized hard drives.
RAID 10
RAID 10 is also known as RAID 1+0, as it combines the benefits of both. This means that you get the best of both worlds in terms of performance and redundancy. The downside of it is that it requires at least four hard disks and also cuts the total storage space in half. Therefore, if you have eight drive bays and fill the entire NAS with hard drives, you will only have half (four total) of the drives as usable storage space.
RAID 10 is an option for people who are using NAS devices with eight or more drive bays. Technically, you can use it if you have fewer drive bays as well, but at a certain point, it just becomes overkill and RAID 5/6 or SHR/SHR-2 becomes a better option.
Conclusion & Final Thoughts: Which RAID to Use on your Synology?
On an overall level, RAID 5 is generally the best and most flexible RAID for Synology NAS devices. This is because it provides redundancy while also allowing you to utilize most of your hard drives for storage space. If you have hard drives that are different sizes or you simply want flexibility, SHR is a great option as well.
RAID 6 is also a RAID type that’s widely used, but you have to ensure that you have enough storage space from your hard drives (and drive bays) before committing to it. With RAID 5, you’ll have one drive that can fail without data loss, and with RAID 6, you’ll have two. As mentioned above, SHR-2 is also an option in cases like this.
When looking at what is the best RAID type for a Synology NAS, the only RAID type I’d suggest that you don’t use is RAID 0. There are performance benefits to it, but the risk of data loss is too high due to the lack of redundancy. Please keep in mind that RAID IS NOT A BACKUP and you want to ensure that you’re always backing up your important data.
Thanks for checking out the article. If you have any questions, please leave them in the comments!




