Raid 1 and 5 are two of the most popular RAID types that you can use, but they’re drastically different. In this article, we’re going to compare RAID 1 vs RAID 5 to determine the best RAID type you can use. Before comparing each in terms of their features, advantages, and disadvantages, we’ll look at exactly how both function.
RAID 1 vs RAID 5: Which RAID Type is Best?
The main difference between RAID 1 and 5 is that RAID 5 stripes data and parity across multiple disks, while RAID 1 mirrors data identically on two or more disks. RAID 5 requires at least three total disks, while RAID 1 only requires two.
However, RAID 5 only uses one total drive for parity, while RAID 1 uses half of the total drives so you’ll end up with more total storage space with RAID 5. We’ll look at RAID 1 and 5 in detail below.
What Is RAID 1?
RAID 1 is a simple mirror configuration where two or more physical disks store the same data. The redundancy comes from the fact that the data is an exact replica (mirror), so when data is written to the first disk(s), it is matched on the second disk(s). This provides redundancy and fault tolerance.
This means that if one disk fails, the other disk(s) can still serve the data without any loss or interruption. RAID 1 also offers high performance, especially for read operations, as any disk can satisfy any read request.
While RAID 1 has a few key benefits, it also has some drawbacks:
- It requires at least two disks, but only half of the total disk capacity is usable for data storage. The rest is “wasted” as duplicate data (which is where the redundancy comes from).
- It does not scale well with an increasing number of disks, as the probability of disk failure increases and the recovery process becomes more complex. Generally, RAID 10 is used for larger storage pools where a mirror is desired.
What Is RAID 5?
RAID 5 is a configuration that uses striping with an individual drive saved for parity and fault tolerance. When using RAID 5, the data is striped into blocks and distributed evenly across multiple disks in the RAID array.
Parity is also used, which calculates an extra block of data and stores it on one of the disks. This can be recovered in case of a disk failure (which is why RAID 5 allows for one disk to fail without losing data).
The parity block is distributed among all disks in the array so that no single disk becomes a single point of failure.
While RAID 5 offers some key benefits, there are some drawbacks as well:
- It requires at least three disks, so if you have a RAID array with two disks, you cannot utilize RAID 5, but only one disk’s capacity is wasted for parity. The rest is available for data storage.
Feature Differences
RAID 1 and 5 are extremely different, but here are some key feature differences when comparing RAID 1 vs RAID 5.
- RAID 1 can be used with two total disks, while RAID 5 requires at least three disks.
- RAID 5 has a slower overall write speed than RAID 1 (which is similar to that of a single disk) due to the parity calculations.
- RAID 5 can have a single disk fail without data loss, while RAID 1 ultimately can have one (or more) disks fail based on the total number of drives being mirrored.
- RAID 5 will have a higher overall storage capacity when comparing RAID arrays of the same total disks due to the fact that only one drive is used for parity. RAID 1 will only have half the available drives usable for storage.
- RAID rebuilds will be faster on RAID 1 than on RAID 5 since the data is mirrored on RAID 1 and parity calculations must be done with RAID 5.
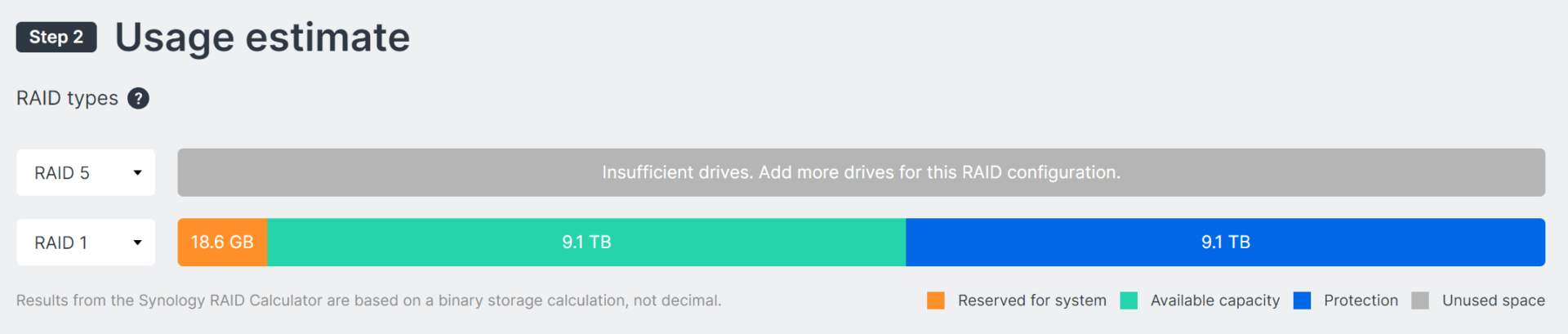
Synology’s RAID Calculator – Three Drives Required for RAID 5
How to Choose Which RAID Type to Use?
The choice between RAID 1 vs RAID 5 depends on the overall requirements you’re trying to hit with your RAID array. Here are some things to consider when deciding:
- Performance: If you need high read and write performance, RAID 1 might be a better option than RAID 5.
- Capacity: If you need more storage space and want to minimize waste, RAID 5 might be a better option than RAID 1.
- Reliability: If you need high reliability and want to avoid data loss at any cost, RAID 1 might be a better option than RAID 5.
- Cost: If you have a limited budget and want to save money on hardware, RAID 5 might be a better option than RAID 1.
Side-by-Side Comparison Between RAID 1 and RAID 5
This chart highlights some key differences between RAID 1 and 5.
| RAID 1 | RAID 5 |
|---|---|
| Mirrors data on two or more disks | Stripes data and parity across multiple disks |
| Provides high read and write performance | Provides fast read but slower write performance |
| Requires at least two disks | Requires at least three disks |
| Wastes half of the total disk capacity | Wastes only one disk’s capacity |
How to Protect Your Data from Potential Risks?
No matter which RAID type you choose, you should always take some precautions to protect your data:
- Backups: You should always backup your data regularly and store it in a separate location (preferably offsite), such as an external hard drive, a cloud service, or another RAID array. With backups, you can restore lost or corrupt data.
- Monitor: You should always monitor the status and performance of your RAID array, especially the overall disk health. This allows you to detect and fix problems before they cause data loss or damage.
- Replace: You should always replace any faulty or degraded disks as soon as possible This ensures that the RAID array has functional drives at all times and disks with errors are replaced as soon as possible.
Conclusion & Final Thoughts: RAID 1 or RAID 5?
This article looked at RAID 1 vs RAID 5 to determine which option is best for data storage. RAID 1 provides high performance and reliability by mirroring data on two or more disks. The downside is that it wastes half of the disk capacity and does not scale well, which is where RAID 5 excels.
RAID 5 provides efficient storage and fast read performance by striping data and parity across multiple disks, but has slower write performance and can only tolerate one disk failure. The choice between RAID 1 and RAID 5 depends on the requirements (performance, storage capacity requirements, reliability, etc). As always, ensure that you back up your important data offsite!
Thanks for checking out the article on RAID 1 vs RAID 5. If you have any questions, please leave them in the comments!




